字符串搜索
主串A: a, b, c, d, e, f, g
模式串B: c, d, e
判断B是否在A中, 存在返回在A中的下标, 不存在返回-1
再如: A: ABCABCAABCABCD; B: ABCABCD; 返回值7.
BF: 暴力破解
复杂度O( (n-m)*m )
1//BF:暴力破解
2 int BF(String A, String B){
3 int aLength = A.length();
4 int bLength = B.length();
5 //这里aLength - bLength稍微优化了一下
6 for (int i = 0; i <= aLength - bLength; i++) {
7 int j;
8 for (j = 0; j < bLength; j++) {
9 if (A.charAt(i+j) != B.charAt(j)){
10 break;
11 }
12 }
13 //需要判断上面的子循环什么时候将B完整遍历了一遍
14 //当j=B.length时, 刚好执行了最后一次j++
15 if(j == B.length()){
16 return i;
17 }
18 }
19 return -1;
20 }
RK算法: hash算法
基于BF进行优化, 将A中的字符串按照顺序截取B字符串的长度: abc, bcd, cde, def, efg. 进行hash运算然后与B的hash值进行比较. 时间复杂度: O(m*n), hash算法参与字符串位数, 主串长度相关.
优化: hash算法: 按26进制取和, abc=1+2+3=6, 进行量化. 每个子串的hash值是前一个子串的hash值-前串最小下标对应字母的值+本串最大下标字母对应的值.
此时间复杂度为O(n), 只与主串长度相关, 但hash冲突极端情况下退化为BF
1//RK:hash算法
2 static int RK(String A, String B){
3 int aLength = A.length();
4 int bLength = B.length();
5 int bCode = B.hashCode();
6 for (int i = 0; i <= aLength - bLength; i++) {
7 String aSub = A.substring(i, i + bLength);
8 if(aSub.hashCode() == bCode){
9 //防止hash碰撞
10 int j;
11 for (j = 0; j < bLength; j++) {
12 if (aSub.charAt(j) != B.charAt(j)){
13 return -1;
14 }
15 }
16 if (j == bLength){
17 return i;
18 }
19 }
20 }
21 return -1;
22 }
23
24 //RK: hash算法 优化hash
25 static int hashCode(String string){
26 int hashCode = 0;
27 //初始化字母表
28 HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
29 int base = (int)'A'-1;
30 for (char c='A'; c<='Z'; c++){
31 map.put(c, (int)c-base);
32 }
33 for (char c='a'; c<='z'; c++){
34 map.put(c, (int)c-base);
35 }
36
37 for (int i = 0; i < string.length(); i++) {
38 hashCode += map.get(string.charAt(i));
39 }
40 return hashCode;
41 }
BM算法
1.坏字符规则: 从右往左匹配, 找到A中第一个不匹配的字符(坏字符), 将B串右移, 直到出现与A串坏字符对齐的字符, 再从右往左寻找坏字符. 如果B串中没有该坏字符, 则直接移到该坏字符的下一位即可.
例如A串:ABCABCAABCABCD; B串ABCDBC. A串前6个为ABCABC, 初始从右往左匹配, 这时B串的C与A串该位置的C对应, 继续匹配B, 然后B串中的D与A串中的对应位置A不匹配, 出现换字符.
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2ABCDBC
于是右移B串, 第一个与A坏字符对应的B串位置就是第一个字母, 现在变成了
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2 ABCDBC
B串往右移动了两格. 又开始从右往左寻找坏字符, 这时第一个B与C就冲突了, 于是又开始右移, 对齐这个坏字符:
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2 ABCDBC
B串往右移动一格后坏字符对齐, 又开始从右往左寻找坏字符, A与D出现冲突, 右移:
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2 ABCDBC
B串右移三格. 这一次再移动一格就到头了, 不行.
坏字符规则是从右往左比较的, 并且这个移动规则保证了跳过多余的比较同时又不会遗留.
2.好后缀规则: 从右往左匹配, 找到坏字符(坏字符后面的串是匹配的, 是好串), 往左寻找B中是否还有该好后缀, 如果有, 将B右移到该位置与A好后缀进行对齐. 重复该规则. 如果B串往右没有该好后缀, 则右移到好后缀的往右错一位的位置, 重复该规则. 避免B串的前缀与好后缀的后缀匹配
还是以上面为例:
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2ABCDBC
这时好串是BC, 往前寻找发现还有这个好后缀, 于是进行对齐:
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2 ABCDBC
这时坏字符是第一个, 没有好串, 只有先对齐了:
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2 ABCDBC
有好串了, 继续
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2 ABCDBC
在移动就超过长度了, 于是没有匹配的.
再举有匹配的一例:
1ABCABCAABCABCD
2ABCABCD
3开始位置0; 坏字符下标:6; 需要移位:3;
4
5ABCABCAABCABCD
6 ABCABCD
7开始位置3; 坏字符下标:6; 需要移位:1;
8
9ABCABCAABCABCD
10 ABCABCD
11开始位置4; 坏字符下标:6; 需要移位:3
12
13ABCABCAABCABCD
14 ABCABCD
15开始位置7; 无坏字符.
两种规则综合使用, 哪种移动的位数多使用哪种
时间复杂度: O(n/m), 最坏O(m*n)
1//BM
2 static int BM(String A, String B){
3 int aLength = A.length();
4 int bLength = B.length();
5 //每次操作结束后A串对齐B串的标志位
6 int index = 0;
7 while (true) {
8 for (int j = bLength-1; j > 0; j--) {
9 //出现坏字符
10 if (A.charAt(index + j) != B.charAt(j)){
11 Boolean ifHaveBad = false;
12 for (int i = j; i > 0; i--) {
13 //B串中有坏字符
14 if (A.charAt(index + j) == B.charAt(i)){
15 ifHaveBad = true;
16 index += j-i;
17 break;
18 }
19 }
20
21 if (!ifHaveBad){
22 //B串中没有坏字符, 应移位到坏字符下一位
23 index += j;
24 }
25
26 //如果已经不能再移位了, 说明没有匹配的.
27 if (aLength - index < bLength) return -1;
28
29 //移位, 进行下一次规则循环比较.
30 break;
31 }
32 //在B串一次循环中没有一次进入if分支, 说明全部匹配
33 return index;
34 }
35 }
36 }
KMP算法
前缀: 字符串A=B+S, S非空, 那么B就是A的前缀
后缀: 字符串A=S+B, S非空, 那么B是A的后缀
PMT值: 前缀集合和后缀集合的交集中, 最长元素的长度
部分匹配表: PMT值集合, 字符串的所有前缀的PMT值
perfix数组: 每一个下标位置对应一个PMT值, 组成的数组
next数组: perfix向右移一个下标位置, 组成next数组
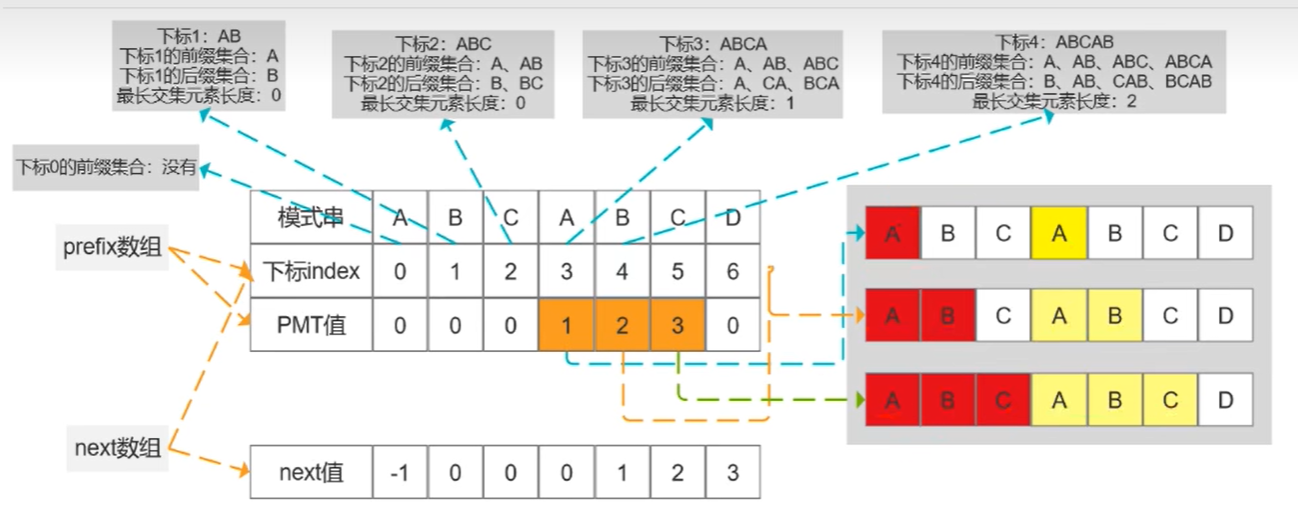
这个PMT值就是我们每次找到坏字符后, pattern字符串需要移动的距离.
求next数组:
1//KMP: next数组生成
2 static void getNext(char[] pattern, int[]next){
3 //next数组其余位置默认是0.
4 next[0] = -1;
5 int i = 0, j = -1;
6
7 while (i < pattern.length){
8 //每当j=-1时, 就是说明当前子串已经找完了.
9 if(j == -1){
10 i++;
11 j++;
12 }else if(pattern[i] == pattern[j]){
13 i++;
14 j++;
15 //这时i位置上的值赋值的是i-1位置上的KMP值, 错位了.
16 next[i] = j;
17 }else {
18 //当字母不匹配后回到这里, j慢慢缩小直到-1.
19 j = next[j];
20 }
21 }
22 }
以ABCABCD串解释如何求出next数组.
1.默认情况下i=0, j=-1, 这时刚好寻找下标为0子串的KMP值, 这是肯定为0的, 所以我们进行i++,j++.
1ABCABCD
2ABCABCD
2.现在变成了i=1, j=0; 由于此时B != A, 说明子串AB的KMP值为0, 于是将j赋值为-1, 这样i就会++. 表明这个位置没有匹配的, 仍需要移动
1ABCABCD
2 ABCABCD
3.现在i=1, j=-1, 又变成i=2, j=0, C!=A, 第一个仍然不匹配, 继续
1ABCABCD
2 ABCABCD
4.现在i=3, j=0, 匹配了, 将next[4] = 1, i++, j++后继续匹配, next[5] = 2, i++, j++后继续匹配, next[6] = 3, 当i=6, j=3时, 不匹配了, 又回到j=0了, 然后j=-1, 最后i = 7 = pattern的长度了.
1ABCABCD
2 ABCABCD
最后一个问题, j = next[j];是否一定会让j变成-1, 有没有例外情况? 我们举例来看看:
1如果串是: ABCABCDABCDA
2
3ABCABCDABCDA
4 ABCABCDABCDA
5这时i=10 j=3时不匹配, 那么j=next[3]=0
初步估计这个next数组是越来越大的, 因为子串的长度在不断增大, KMP值越来越大, 所以它总会收敛于-1的.
算法本体:
1//KMP
2 static int search(char[] str, char[] pattern, int[] next){
3 int i = 0;
4 int j = 0;
5
6 while (i < str.length && j < pattern.length){
7 if (j == -1 || str[i] == pattern[j]){
8 i++;
9 j++;
10 }else {
11 //不匹配了 , 就往后移动.
12 //所以下标0的-1也是移动的手段,
13 j = next[j];
14 }
15 }
16
17 //如果j最后一直到了最后都和i匹配, 说明找到了.
18 if (j == pattern.length){
19 return i - j;
20 }else {
21 return -1;
22 }
23 }
测试:
1public static void main(String[] args) {
2 String A = "ABCABCAABCABCD";
3 String B = "ABCABCD";
4 System.out.println(BF(A, B));
5 System.out.println(RK(A, B));
6 //System.out.println(hashCode(B));
7 System.out.println(BM(A,B));
8
9 int[] next = new int[B.length()];
10 getNext(B.toCharArray(), next);
11 int i = search(A.toCharArray(), B.toCharArray(), next);
12 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(next));
13 System.out.println(i);
14 System.out.println(A.indexOf(B));
15 }
打家劫舍
动态规划三要素:
- 最优子结构: 每一个问题的最优解都包含子问题的最优解(n的最优依赖的是n-1的最优)
- 递推公式(状态转移方程): 找问题的规律, 解和前面解的关系
- 重叠子问题
初始问题
问题: 小偷偷钱, 不能偷相邻的房间. 给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组, 计算你不触动警报装置的情况下, 一夜能偷窃到的最高金额
输入: [1,2,3,1] 输出:4
输入:[2,7,9,3,1] 输出12
1public class Rob {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 int[] num = new int[]{100, 2, 1, 100};
5 int index = num.length -1;
6 System.out.println(maxMoney(num, index));
7 System.out.println(maxMoney2(num));
8 }
9
10
11 static int maxMoney(int[] num, int index){
12 if (num == null || index < 0){
13 return 0;
14 }
15 if (index == 0){
16 return num[index];
17 }
18 return Math.max(maxMoney(num, index-1), num[index]+maxMoney(num, index-2));
19 }
20
21 static int maxMoney2(int[] num){
22 //健壮性
23 int length = num.length;
24 if (num == null || length == 0){
25 return 0;
26 }
27 if (length == 1){
28 return num[length-1];
29 }
30
31 //dp数组, 存放以及计算的值, 优化计算
32 int[] dp = new int[num.length];
33 dp[0] = num[0];
34 dp[1] = Math.max(num[0], num[1]);
35 for (int i = 2; i <length; i++) {
36 dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1], dp[i-2]+num[i]);
37 }
38
39 return dp[length-1];
40 }
41
42 //优化空间复杂度, 只放两个位置.
43 static int maxMoney3(int[] num){
44 //健壮性
45 int length = num.length;
46 if (num == null || length == 0){
47 return 0;
48 }
49 if (length == 1){
50 return num[length-1];
51 }
52
53 //只需要两个变量, 优化空间复杂度从O(n)到O(1)
54 int first = num[0];
55 int second = Math.max(num[0], num[1]);
56 for (int i = 2; i <length; i++) {
57 int temp = second;
58 second = Math.max(second, first+num[i]);
59 first = temp;
60 }
61
62 return second;
63 }
64}
65
首尾相连
街道房间是圆形的. 第一个和最后一个也算是相邻的.
由于第一个和最后一个是互斥的, 于是分解为两个子问题: 第一个房子到倒数第二个房子的最优解, 与第二个房子到最后一个房子的最优解. 分别求出来比较大小.
1public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int[] num = new int[]{100, 2, 1, 100};
3 System.out.println(Math.max(
4 maxMoney4(num, 0, num.length-2),
5 maxMoney4(num, 1, num.length-1)
6 ));
7 }
8
9
10//将下标作为变量, 分别进行最优解运算.
11 static int maxMoney4(int[] num, int start, int end){
12 //健壮性
13 int length = num.length;
14 if (num == null || length == 0){
15 return 0;
16 }
17 if (length == 1){
18 return num[length-1];
19 }
20
21 //只需要两个变量, 优化空间复杂度从O(n)到O(1)
22 int first = num[start];
23 int second = Math.max(num[start], num[start+1]);
24 for (int i = start+2; i <= end; i++) {
25 int temp = second;
26 second = Math.max(second, first+num[i]);
27 first = temp;
28 }
29
30 return second;
31 }
二叉树
父子关系就是相邻的情况.
1public static void main(String[] args) {
2 TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(1, null, null);
3 TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(3, null, null);
4 TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(3, null, node5);
5 TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(2, null, node4);
6 TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(3, node2, node3);
7 //传入根节点
8 int[] dfs = dfs(node1);
9 System.out.println(Math.max(dfs[0], dfs[1]));
10 }
11
12
13//深度优先算法
14 public static int[] dfs(TreeNode node){
15 //int[]两个值, 一是选了这个节点select的最优解,第二个是没选这个节点not select的最优解
16 if (node == null){
17 //如果是null节点, 选与不选结果都是1.
18 return new int[]{0,0};
19 }
20 int[] l = dfs(node.left);
21 int[] r = dfs(node.right);
22 //选这个节点意味着不能选下面的节点
23 int select = node.val + l[1] + r[1];
24 //不选这个节点意味着选子节点, 选子节点最大的情况.
25 int notSelect = Math.max(l[0], l[1]) + Math.max(r[0], r[1]);
26 return new int[]{select, notSelect};
27 }
反转链表
1.迭代
用变量保存当前节点和下一个节点的信息, 以此赋值.
1public class ReverseList {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5, null);
5 ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4, node5);
6 ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3, node4);
7 ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2, node3);
8 ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1, node2);
9 ListNode iterate = iterate(node1);
10 }
11
12 static class ListNode{
13 int val;
14 ListNode next;
15
16 public ListNode(int val, ListNode next){
17 this.val = val;
18 this.next = next;
19 }
20 }
21
22 public static ListNode iterate(ListNode head){
23 //保存前一个节点
24 ListNode pre = null;
25 //保存当前节点
26 ListNode curr = head;
27 ListNode next;
28 while (curr != null){
29 //先保存下一个节点的信息, 避免被覆盖
30 next = curr.next;
31 //在pre还未指向新的pre之前给自己赋值
32 curr.next = pre;
33 pre = curr;
34 curr = next;
35 }
36 return pre;
37 }
38
39
40}
41
2.递归
以相似的方式重复, 类似于树结构, 从最里面开始遍历.
1public static ListNode recursion(ListNode head){
2 if (head == null || head.next == null){
3 return head;
4 }
5 //从最后往前修改
6 ListNode new_head = recursion(head.next);
7 head.next.next = head; // 后一个指向前一个
8 head.next = null; //断原来的链
9 return new_head;
10 }
素数个数统计
1.暴力算法
对每个数字x继续筛选, 看x是否会被小于根号x的数字整除. 可以用i * i < x 表示根号.
1public class PrimeSearch {
2
3
4 public static int bf(int x){
5 int count = 0;
6 for (int i = 2; i <= x; i++) {
7 count += isPrime(i) ? 1 : 0;
8 }
9 return count;
10 }
11
12 private static boolean isPrime(int i) {
13 for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++) {
14 if (i % j == 0){
15 return false;
16 }
17 }
18 return true;
19 }
20}
21
2.埃氏筛选
埃氏筛选: 找到一个质数, 立刻将这个质数所有的倍数都淘汰为合数.
1 public static int eratosthenes(int n){
2 int count = 0;
3 //由于数组下标的因素, 设置为n+1
4 Boolean[] isPrime = new Boolean[n+1]; //初始化为false
5 Arrays.fill(isPrime, true); //所有默认为true
6 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
7 if (isPrime[i]){
8 count++;
9 //排除所有这个质数的倍数的合数.
10 for (int j = i*i; j <= n; j+=i) {
11 isPrime[j] = false;
12 }
13 }
14 }
15 return count;
16 }
删除排序数组中的重复项
一个有序数组nums, 原地删除重复出现的元素, 使每个元素只出现一次, 返回删除后数组的新长度
不能使用额外的数组空间, 必须在原地修改数组并在使用O(1)额外空间的条件下完成.
输入: [0,1,2,2,3,3,4]
输出: 5
Java中没有数组元素删除操作, 删除了只能置为null. 或者只能新建数组拷贝.
双指针算法: i(慢指针)和j(快指针)依次指向第一个和第二个, 如果他们对应元素不相等, 则都+1; 如果对应元素相等, 那么j+1; 如果是相等之后出现了不相等, 那么这时将j所在位置的元素赋值给i+1所在位置的元素(nums[i+1]=nums[j]); 如果j到了最后一个, 则返回i.
1public class SortedArrayDuplicates {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 System.out.println(
5 removeDuplicates(new int[]{0,1,2,2,2,3,3,4})
6 );
7 }
8
9 public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums){
10 if (nums.length == 0){
11 return 0;
12 }
13
14 int i = 0;
15 for (int j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
16 //当不相等时, 如果是挨着的, 那么nums[i] = nums[j];无影响
17 //如果不是挨着的, 那么会将重复的元素赋值为下一个不重复的元素
18 if (nums[i] != nums[j]){
19 i++;
20 nums[i] = nums[j];
21 }
22 }
23
24 return i + 1;
25 }
26}
27
寻找数组的中心下标
给定一个整数数组nums, 返回数组"中心下标"的方法, 不存在返回-1, 有多个则返回最靠近左边的那个.
中心下标是数组的一个下标, 其左侧的所有元素相加的和等于右侧所有元素相加的和. 中心下标可能出现在数组的两端.
这道题的关键是理解题意, 左边等于右边, 这是不包括当前位置的值的. 于是思路有
-
轮到下标为i元素时, 判断0+1+..+i-1+ i 是否等于 sum - 0 - 1 - (i-1). 双方都加一个当前元素等于没有加.
1public static int pivotIndex(int[] nums){ 2 int sumMinusPrev = Arrays.stream(nums).sum(); 3 int leftPlusCurr = 0; 4 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 5 leftPlusCurr += nums[i]; 6 if (leftPlusCurr == sumMinusPrev){ 7 return i; 8 } 9 sumMinusPrev -= nums[i]; 10 } 11 return -1; 12 } -
既然左边右边是相等的, 那么2*(0+1+2+…+i-1) + i = sum总和.
1public static int pivotIndex2(int[] nums){ 2 int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum(); 3 int ima = 0; 4 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){ 5 if (ima * 2 + nums[i] == sum){ 6 return i; 7 } 8 ima += nums[i]; 9 } 10 return -1; 11 }
验证:
1public static void main(String[] args) {
2 System.out.println(pivotIndex(new int[]{1,7,3,6,5,6}));
3 System.out.println(pivotIndex2(new int[]{1,7,3,6,5,6}));
4 }
X的平方根
不使用sqrt函数, 得到x的平方根的整数部分.
二分法
寻找i * i < x 但 (i+1)*(i+1) > x的值, 使用二分法缩减寻找次数.
1public static int binarySearch(int x){
2 int index = -1;
3 int lP = 0, rP = x;
4 while (lP <= rP){
5 //计算新的左右指针的中间值
6 int mid = (lP + rP) / 2;
7 if (mid * mid <= x){
8 lP = mid + 1;
9 //取小值
10 index = mid;
11 }else {
12 rP = mid - 1;
13 }
14
15 }
16 return index;
17 }
牛顿迭代
原理: x/n 与 n的均值比他们原来更趋近于根号x.
原本的牛顿迭代是迭代选取的点对应切线与x轴交点的值(x1 = x0 - f(x0)/df(x0)),
这里相当于是求x^2-x0=0方程的根, 化简之后就是(i + x/i)/2, 和牛顿迭代一致.
1public static int newton(int x){
2 //第一个参数值无所谓, 越接近根号x, 则迭代次数越少.
3 return (int)sqrt(x, x);
4 }
5
6 public static double sqrt(double i, int x){
7 double res = (i + x/i)/2;
8 if (res == i){
9 return res;
10 }else {
11 sqrt(res, x);
12 }
13 }
数组中三个数的最大乘积
整形数组nums, 在数组中找出由三个数字组成的最大乘积, 并输出.
当数组全为整数时, 最大乘积为前三个最大的数的乘积;
当数组有一个负数时, 最大乘积为前三个最大的数的乘积;
当数组由两个及以上的负数时, 最大乘积为前三个最大的数的乘积 和 最大的数与两个最小的数的乘积之大者.
先排序后计算
算法复杂度取决于排序算法.
1public static int sortAndCalc(int[] nums){
2 int length = nums.length;
3 Arrays.sort(nums);
4 return Math.max(
5 nums[0]*nums[1]*nums[length-1],
6 nums[length-1]*nums[length-2]*nums[length-3]
7 );
8 }
线性扫描: 只找出前三最大和前二最小
1public static int getMax3AndMin2(int[] nums){
2 int max1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, max3 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
3 int min1 = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min2 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
4 for (int num : nums){
5 if (num > max1){
6 max3 = max2;
7 max2 = max1;
8 max1 = num;
9 }else if (num > max2){
10 max3 = max2;
11 max2 = num;
12 }else if (num > max3){
13 max3 = num;
14 }
15
16 if (num < min1){
17 min2 = min1;
18 min1 = num;
19 }else if (num < min2){
20 min2 = num;
21 }
22 }
23
24 return Math.max(
25 max1*max2*max3,
26 max1*min1*min2
27 );
28 }
两数之和–无序数组
给定整数数组nums, 从中寻找两个数满足他们之和为给定目标target.
不可重复使用元素, 返回两数的下标值, 以数组形式返回.
可以使用暴力算法.
或者利用map记录扫描过的数及下标. 这样空间复杂度会稍高.
1import java.util.Arrays;
2import java.util.HashMap;
3import java.util.Map;
4
5public class TwoNumberForSum {
6
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 System.out.println(
9 Arrays.toString(solution(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, 10))
10 );
11 }
12
13
14 public static int[] solution(int[] nums, int target){
15 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
16 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
17 if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){
18 return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
19 }
20 map.put(nums[i], i);
21 }
22 return new int[0];
23 }
24}
25
两数之和–有序数组
二分查找
遍历左边的界限, 在界限之中应用二分查找target-nums[i]的数.
1public static int[] twoSearch(int[] nums, int target){
2 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
3 int low = nums[i], high = nums.length - 1;
4 while (low <= high){
5 int mid = (low + high) / 2;
6 if (nums[mid] == target - nums[i]){
7 return new int[]{i, mid};
8 }else if (nums[mid] > target - nums[i]){
9 high = mid - 1;
10 }else {
11 low = mid + 1;
12 }
13 }
14 }
15 return new int[0];
16 }
双指针
前提是有序.
1public static int[] twoPointer(int[] nums, int target){
2 int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
3 while (low < high){
4 int sum = nums[low] + nums[high];
5 if (sum == target){
6 return new int[]{low, high};
7 }else if (sum > target){
8 high--;
9 }else {
10 low++;
11 }
12 }
13 return new int[0];
14 }
计算斐波那契数列
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, …. 后一项等于前面两项的和.
暴力递归
直接递归, 这样有些项存在严重的重复计算.
1public static int BFRecursion(int num){
2 if (num == 0) return 0;
3 if (num == 1) return 1;
4 return BFRecursion(num - 1) + BFRecursion(num - 2);
5 }
去重递归
用空间保存计算过的项. 时间O(n) 空间O(n)
1public static int SavedRecursion(int num){
2 //由于第一个是0, 所以需要多一个空间.
3 int[] saveArr = new int[num + 1];
4 return Recursion(saveArr, num);
5 }
6
7 private static int Recursion(int[] saveArr, int num) {
8 if (num == 0) return 0;
9 if (num == 1) return 1;
10 //如果之前这个位置已经被运算, 直接返回.
11 if (saveArr[num] != 0) return saveArr[num];
12 saveArr[num] = Recursion(saveArr, num - 1) + Recursion(saveArr, num - 2);
13 return saveArr[num];
14 }
双指针迭代
只需要两个位置保存, 节省了空间至O(1)
1public static int TwoPointer(int num){
2 if (num == 0) return 0;
3 if (num == 1) return 1;
4 int first = 1, second = 0;
5 for (int i = 2; i <= num; i++) {
6 int temp = first;
7 first = first + second;
8 second = temp;
9 }
10 return first;
11 }
排列硬币
n枚硬币, 将他们排列为阶梯形状, 第k行有k枚硬币.
给定一个数字n, 找出可形成完整阶梯行的总行数. 就是可以剩, 不需要全部用完.
暴力迭代
啥也不管, 一行一行地排
1public static int arrangeCoinBF(int n){
2 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
3 n -= i;
4 if (n < i + 1){
5 return i;
6 }
7 }
8 return -1;
9 }
二分查找
行数必定在0到n之间, 查找这之中满足求和=n的值, 找不到就返回最大的行使求和<n.
1public static int arrangeCoinSearch(int n){
2 int low = 0, high = n - 1;
3 while (low < high){
4 int mid = (low + high) / 2;
5 int predict = ((mid + 1) * mid) / 2;
6 if (n == predict){
7 return mid;
8 }else if (n < predict){
9 high = mid - 1;
10 }else {
11 low = mid + 1;
12 }
13 }
14 return low;
15 }
牛顿迭代
给定总数n求行数x, 由于 (x^2 + x) /2= n, 想求对应的x, 实际上是函数f(x) = (x^2 + x) /2 - n的根, 于是可以采用牛顿迭代, 每次迭代x1 = x0 - f(x0)/df(x0) = (x0^2 + 2n)/(2x0+1), 如果从n开始迭代, 则第一次为
1public static double newtonRecursion(int n, int res){
2 res = (res * res + 2 * n) / (res * 2 + 1);
3 if (res * res + res == 2 * n){
4 return res;
5 }else {
6 return newtonRecursion(n, res);
7 }
8 }
环形链表
给定额链表, 判断链表中是否有环(如果链表有某个节点可以通过连续跟踪next指针再次到该节点, 就存在环). 存在环返回true, 否则返回false.
内部类:
1//内部类
2 static class ListNode{
3 int val;
4 ListNode next;
5
6 public ListNode(int val, ListNode next){
7 this.val = val;
8 this.next = next;
9 }
10 }
11
12 public static void main(String[] args) {
13 ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5, null);
14 ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4, node5);
15 ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3, node4);
16 ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2, node3);
17 ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1, node2);
18 //node5.next = node3;
19
20 System.out.println(isCycle(node1));
21 System.out.println(isCycleTwoPointer(node1));
22 }
普通循环
时间O(n), 空间O(n)
1public static Boolean isCycle(ListNode head){
2 HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
3 while (head != null){
4 if (!set.add(head)){
5 return true;
6 }
7 head = head.next;
8 }
9 return false;
10 }
双指针
如果快指针和慢指针可以重叠, 说明存在环; 如果快指针到达了null, 说明没有环.
时间O(n), 空间O(1)
1public static Boolean isCycleTwoPointer(ListNode head){
2 if (head == null || head.next == null) return false;
3 ListNode slow = head;
4 ListNode fast = head.next;
5 while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
6 if (slow == fast) return true;
7 slow = slow.next;
8 fast = fast.next.next;
9 }
10 return false;
11 }
合并两个有序数组
两个有序整数数组nums1和nums2, 将nums2合并到nums1中, 使nums1成为一个有序数组. nums1和nums2元素个数分别为m和n, 假设nums1的空间大小等于m+n.
合并后排序
取决于排序的时间复杂度O(N*logN), 不消化额外空间
1//m为nums1实际元素个数, n为nums2实际元素个数
2 public static int[] mergeAndSort(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n){
3 //将数组2拷贝至数组1的后面.
4 System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, m, n);
5 //排序, 复杂度取决于排序的复杂度, 为N*logN
6 Arrays.sort(nums1);
7 return nums1;
8 }
双指针
需要消耗O(n)的空间
1public static int[] compareAndInsert(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n){
2 //要求返回nums1, 所以我们需要处理一下.
3 int[] num1Copy = new int[m];
4 System.arraycopy(nums1, 0, num1Copy, 0, m);
5 int pointerNum1 = 0, pointerNum2 = 0;
6 int i = 0;
7// int[] res = new int[m+n];
8
9 while (pointerNum1 < m && pointerNum2 < n){
10 //被选中的才会++, 且是先用后++.
11 nums1[i++] = num1Copy[pointerNum1] < nums2[pointerNum2] ? num1Copy[pointerNum1++] : nums2[pointerNum2++];
12// if (nums1[pointerNum1] > nums2[pointerNum2]){
13// res[i] = nums2[pointerNum2];
14// pointerNum2++;
15// }else {
16// res[i] = nums1[pointerNum1];
17// pointerNum1++;
18// }
19// i++;
20 }
21 if (pointerNum2 < n){
22 System.arraycopy(nums2, pointerNum2, nums1, pointerNum1 + pointerNum2, m + n - pointerNum2 -pointerNum1);
23 }
24 if (pointerNum1 < m){
25 System.arraycopy(num1Copy, pointerNum1, nums1, pointerNum1 + pointerNum2, m + n - pointerNum2 -pointerNum1);
26 }
27 return nums1;
28 }
倒着排
1 public static int[] reverseMerge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
2 int p1 = m - 1, p2 = n-1;
3 int i = m+n-1;
4
5 while (p1 >= 0 && p2 >= 0) {
6 nums1[i--] = nums1[p1] > nums2[p2] ? nums1[p1--] : nums2[p2--];
7 }
8 //有两种情况, 1是nums2下标先走完至-1, 这时无序任何操作
9 //2是nums1下标先走完至-1, 这是nums2还有额外的元素需要复制
10 System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, 0, p2 + 1);
11 return nums1;
12 }
子数组最大平均数
给一个整数数组, 找出平均数最大且长度为k的下标连续的子数组, 并输出该最大平均数.
输入: [1,12,-5,-6,50,3], k=4
输出: 12.75
最大平均数 (12-5-6+50)/4=12.75
滑动窗口
是双指针的特例:
1public static double twoPointer(int[] nums, int k){
2 int pl = 0, pr = k-1;
3 int maxSum = 0;
4 for (int i = pl; i <= pr; i++) {
5 maxSum += nums[i];
6 }
7
8 while (pr < nums.length - 1){
9 int tempSum = maxSum -nums[pl] + nums[pr+1];
10 if (tempSum > maxSum) maxSum = tempSum;
11 pl++;
12 pr++;
13 }
14
15 return 1.0 * maxSum/k;
16 }
由于长度固定, 故只需要一个指针:
1public static double slideWindow(int[] nums, int k){
2 int sum = 0;
3 for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
4 sum += nums[i];
5 }
6 int max = sum;
7
8 for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
9 sum = sum - nums[i-k] + nums[i];
10 max = Math.max(sum, max);
11 }
12
13 return 1.0 * max/4;
14 }
二叉树的最小深度
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量.
深度优先
先找到叶子节点, 然后从叶子节点往上找, 计算每个节点的最小深度(取左右叶子节点较小的那个+1.
空间复杂度O(logN) 取决于树的深度, 时间复杂度O(N)
1 public static int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
2 //空节点
3 if (root == null) return 0;
4 //叶子节点
5 if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
6
7 int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
8 //寻找左右子节点中最小的深度
9 if (root.left != null) min = Math.min(min, minDepth(root.left));
10 if (root.right != null) min = Math.min(min, minDepth(root.right));
11
12 //最后加上本节点的1返回.
13 return min + 1;
14 }
广度优先
一层一层遍历, 遍历到的第一个叶子节点就是最小深度.
空间复杂度取决于队列O(N), 时间复杂度O(N)
1public static int minWidth(TreeNode root){
2 if (root == null) return 0;
3
4 //由于队列的性质, 它是广度遍历. 遍历完同一层才会遍历下一层
5 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
6 root.setDeep(1);
7 //入队
8 queue.offer(root);
9
10 while (!queue.isEmpty()){
11 //出队
12 TreeNode node = queue.poll();
13
14 //遍历到根节点直接返回
15 if (node.left == null && node.right == null){
16 return node.deep;
17 }
18
19 if (node.left != null) {
20 node.left.setDeep(node.getDeep() + 1);
21 queue.offer(node.left);
22 }
23 if (node.right != null){
24 node.right.setDeep(node.getDeep() + 1);
25 queue.offer(node.right);
26 }
27 }
28
29 //非正常退出
30 return -1;
31 }
最长连续递增序列
给定一个未排序的整数数组, 找到最长且连续递增的子序列, 并返回该序列的长度.
方式一: 记录当前序列的开始位置, 如果后面的数字小于这个序列最后一个数, 则更新开始下标.
方式二: 直接记录最大序列的长度和当前序列的长度.
1public class MaxSeq {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 System.out.println(findLength(new int[]{1,2,3,2,3,4,3,4,5,6,7}));
5 }
6
7 public static int findLength(int[] nums){
8 int start = 0;
9 int max = 0;
10 for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
11 if (nums[i] < nums[i-1]) start = i;
12 max = Math.max(max, i - start + 1);
13 }
14 return max;
15 }
16}
17
柠檬水找零
每杯柠檬水5美元, 顾客排队买, 顾客只会付5, 10, 20美元, 必须给顾客正确找零. 一开始手里面没有任何零钱, 如果能正确找零返回true, 否则返回false.
分析: 对于顾客付的5美元, 直接收下; 对于顾客付的10美元, 只能找5美元; 对于20美元, 可以三个5, 也可以10+5, 但是为了局部最优, 最好10+5. 因为这里5是万能的, 尽量减少使用.
1public class LemonWater {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 System.out.println(isCanGiveChange(new int[]{5,5,5,20}));
5
6 }
7
8 public static boolean isCanGiveChange(int[] nums){
9 //5和10的票子数量
10 int fiveNum = 0, tenNum = 0;
11 for (int num: nums) {
12 switch (num){
13 case 5:
14 fiveNum++;
15 break;
16 case 10:
17 if (fiveNum > 0){
18 fiveNum--;
19 tenNum++;
20 }else
21 return false;
22 break;
23 case 20:
24 if (fiveNum > 0 && tenNum > 0){
25 fiveNum--;
26 tenNum--;
27 }else if (fiveNum >= 3){
28 fiveNum -= 3;
29 }else
30 return false;
31 }
32 }
33
34 return true;
35 }
36}
37
三角形的最大周长
给一个正数数组arr, 返回由其3个数组成的, 面积不为0的三角形的周长可能的最大值.
直接找最大和的三个数, 看看是否能形成三角形, 不行就减少最大数继续. 因为既然最大的三个数不行, 那么前两最大的数和任何一个数都不行了, 所以只能往下找.
1import java.util.Arrays;
2
3public class Triangle {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 System.out.println(maxPerimeter(new int[]{3,6,3,2}));
7 }
8
9 public static int maxPerimeter(int[] nums){
10 Arrays.sort(nums);
11 for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 2 ; i--) {
12 if (nums[i-1] + nums[i-2] > nums[i]){
13 return nums[i] + nums[i-1] + nums[i-2];
14 }
15 }
16 return 0;
17 }
18}
19
二叉树遍历
前序
递归实现
1//前序:根左右
2 public static void preorder(TreeNode root){
3 if (root == null) return;
4
5 System.out.println(root.val);
6 preorder(root.left);
7 preorder(root.right);
8 }
中序
递归实现
1 //中序
2 public static void midorder(TreeNode root){
3 if (root == null) return;
4
5 if (root.left != null){
6 preorder(root.left);
7 }
8
9 System.out.println(root.val);
10
11 if (root.right != null){
12 preorder(root.right);
13 }
14
15 }
后序
递归实现
1//后序
2 public static void postorder(TreeNode root){
3 if (root == null) return;
4
5 if (root.left != null){
6 preorder(root.left);
7 }
8
9 if (root.right != null){
10 preorder(root.right);
11 }
12
13 System.out.println(root.val);
14 }
层序
递归实现
1//层序遍历
2 //这个参数i代表的第几层, 由于树不是完全的, 所以一定之间会有null值
3 public static void levelorder(TreeNode root, int i, ArrayList list){
4 if (root == null) return;
5
6 int length = list.size();
7 //为防止数组越界, 这里提前填充至i.
8 if (length <= i){
9 for (int j = 0; j <= i - length; j++) {
10 list.add(length+j, null);
11 }
12 }
13
14 list.set(i, root.val);
15 levelorder(root.left, 2*i, list);
16 levelorder(root.right, 2*i+1, list);
17 }